SQL Server 2022 : AlwaysOn Availability Groups #32023/01/20 |
|
Configure AlwaysOn Availability Groups.
This example is based on the environment with 2 SQL Servers like follows.
(possible to configure with more than 3 SQL Servers)
|
+----------------------+ |
| [ AD DS ] |10.0.0.100 |
| fd3s.srv.world +-----------+
| | |
+----------------------+ |
|
+----------------------+ | +----------------------+
| [ SQL Server #1 ] |10.0.0.101 | 10.0.0.102| [ SQL Server #2 ] |
| rx-7.srv.world +-----------+-----------+ rx-8.srv.world |
| | | |
+----------------------+ +----------------------+
|
|
Configure following settings on a Node you'd like to set as the primary Node of AlwaysOn Availability Groups.
|
|
| [1] | Logon to a Windows Host that SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is installed with a domain user who is set as the admin account of SQL Server, and then
connect to the Primary Node of AlwaysOn Availability Groups with Windows Authentication. Next, right click [Always On High Availability] - [Availability Groups] to open the menu, then click [New Availability Group Wizard]. |

|
| [2] | Click [Next] button. |

|
| [3] | Input any name you like on [Availability group name] and proceed to next. |

|
| [4] | Select databases for Alwayson availability group. |

|
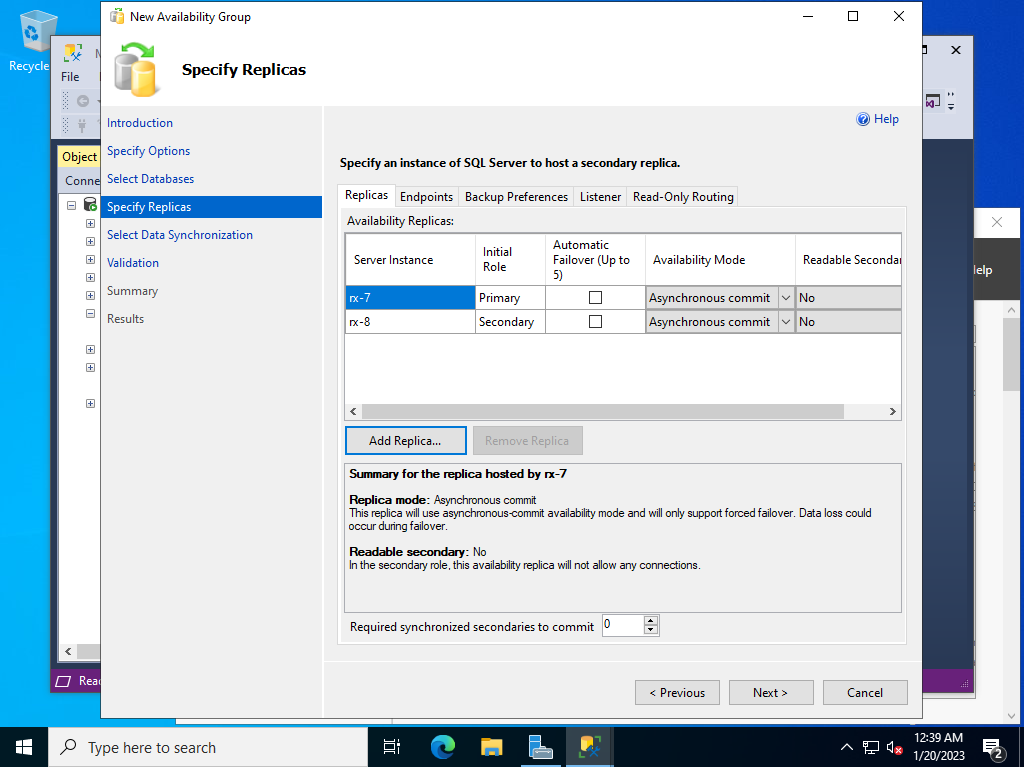
| [5] | Specify replicas. Click [Add Replica] button and specify replica Hosts. |

|
| [6] | After adding all replicas, move to the [Listener] tab. |
|
| [7] | Input any listener name you like on [Listener DNS Name] and also input a listening port on [Port] field. Furthermore, set an IP address for the listener. |

|
| [8] | Select data synchronization preference. It selects [Automatic seeding] on this example. |

|
| [9] | The validation actions run before applying settings. That's OK if all are [Success]. |

|
| [10] | Confirm summary of settings and if that's OK, click [Finish] button to apply settings. |

|
| [11] | After finishing successfully, click [Close] button. |

|
| [12] | It's possbile to see the status of Availability group on SSMS. |

|
| [13] | Verify to access to the listener in order to connect to SQL Server Database Instance. |

|
Matched Content